前言
1、分布式架构面临的问题
微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务, 每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务。于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能运行,所以一套集中式的、动态的配置管理设施是必不可少的。
配置中心架构图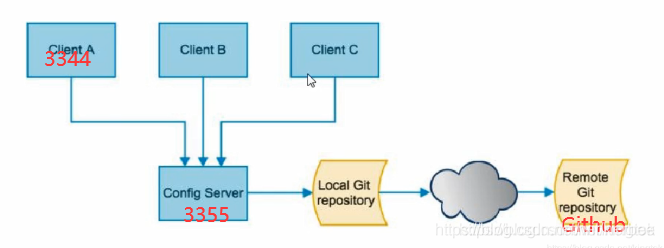
SpringCloud Config为微服务架构中的微服务提供集中化的外部配置支持,配置服务器为各个不同微服务应用的所有环境提供了一个中心化的外部配置。
2、Config能干吗?
- 集中管理配置文件
- 不同环境不同配置,动态化的配置更新,分环境部署比如dev/test/prod/beta/release
- 运行期间动态调整配置,不再需要在每个服务部署的机器上编写配置文件,服务会向配置中心统一一拉取配置自己的信息
- 当配置发生变动时,服务不需要重启即可感知到配置的变化并应用新的配置
- 将配置信息以REST接口的形式暴露
服务端模块 cloud-config-center-3344
1、目录结构
2、改POM
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> 3、建application.yml
server: port: 3344 spring: application: name: cloud-config-center cloud: config: server: git: #uri: git@github.com:zzyybs/springcloud-config.git #Github上的git仓库名字 uri: https://github.com/zzyybs/springcloud-config ##搜索目录.这个目录指的是github上的目录 search-paths: - springcloud-config ##读取分支 label: master eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/ 4、主启动类
package com.atguigu.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer; @EnableConfigServer @SpringBootApplication public class ConfigCenterMain3344 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigCenterMain3344.class,args); } } 5、运行代码
http://localhost:3344/master/config-dev.yml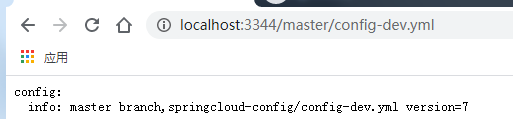
6、总结
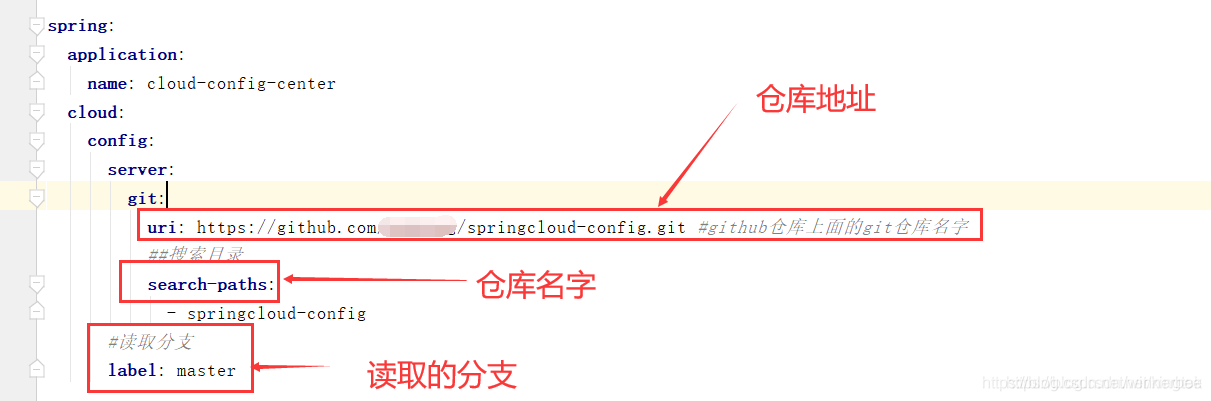
当启动我们的3344项目时,可以通过三种方法找到配置文件并读取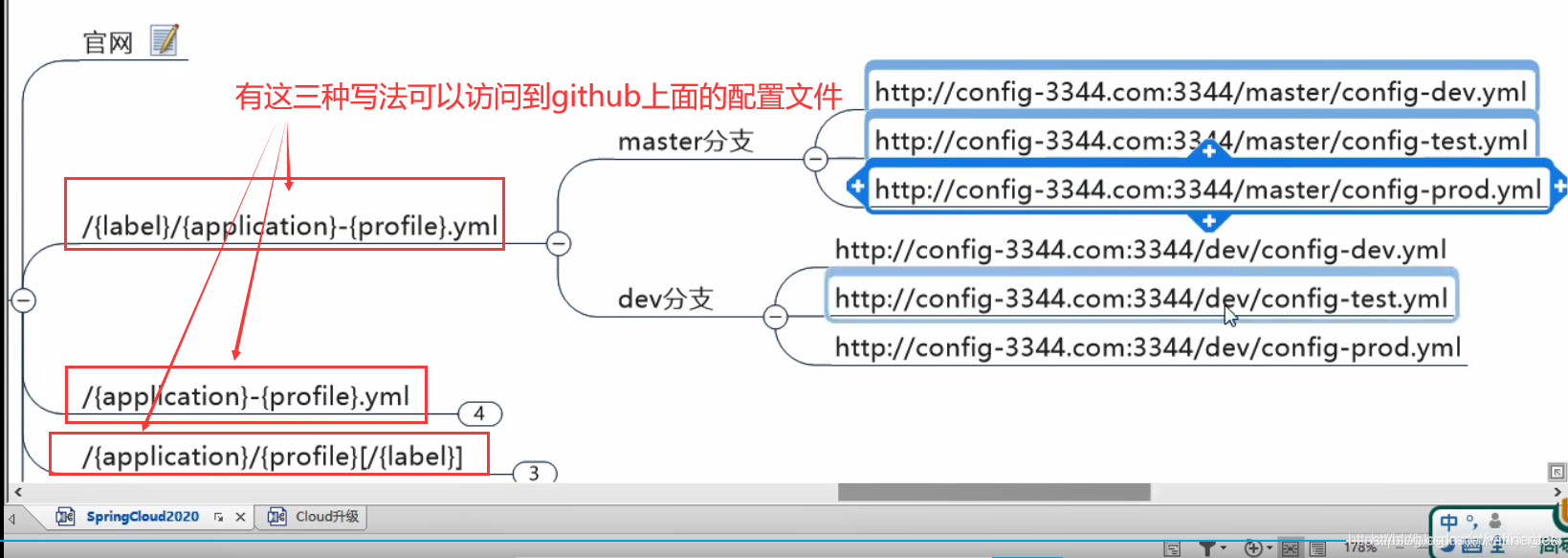
客户端模块 cloud-config-client-3355
- applicaiton. yml是用户级的资源配置项
- bootstrap. yml是系统级的,优先级更加高
Spring Clould会创建一个"Bootstrap Context" , 作为Spring应用的Application Context的父上下文。初始化的时候,BootstrapContext’负责从外部源加载配置属性并解析配置。这两个上下文共享一个从外部获取的Environment。
‘Bootstrap’属性有高优先级,默认情况下,它们不会被本地配置覆盖。 Bootstrap context’和Application Context有着不同的约定,所以新增了一个bootstrap.ymI文件, 保证Bootstrap Context’和Application Context配置的分离。
要将Client模块下的application.yml文件改为bootstrap.yml,这是很关键的,
因为bootstrap.ym是比application.yml先加载的。bootstrap.yml优先级高于application.yml
1、目录结构
2、改POM
<dependencies> <!--不带server了,说明是客户端--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> 3、建bootstrap.yml
server: port: 3355 spring: application: name: config-client cloud: #Config客户端配置 config: label: master #分支名称 name: config #配置文件名称 profile: dev #读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取 http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml uri: http://localhost:3344 #配置中心地址 表示通过这个服务端访问 #服务注册到eureka地址 eureka: client: register-with-eureka: true service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka7001.com:7001/eureka/ 4、主启动类
package com.atguigu.springcloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient; @EnableEurekaClient @SpringBootApplication public class ConfigCenterMain3355 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigCenterMain3355.class,args); } } 5、业务类
package com.atguigu.springcloud.controller; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class ConfigClientController { @Value("${config.info}") private String configInfo; //要访问的3344上的信息 @GetMapping("/configInfo") //请求地址 public String getConfigInfo(){ return configInfo; } } 6、运行代码
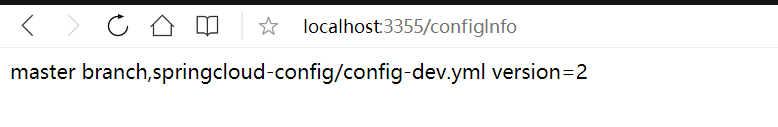
http://localhost:3355/configInfo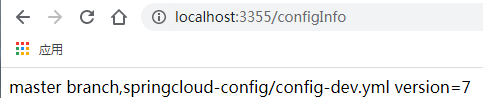
分布式配置动态刷新 cloud-config-client-3355
1、改POM
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> 2、改bootstrap.yml
#暴露监控端点 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: "*" 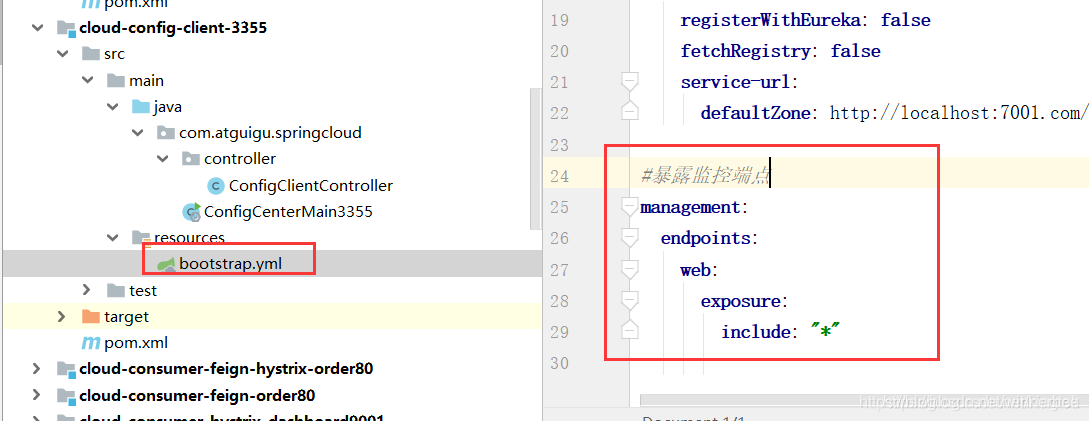
3、业务类
controller层新增一个注解@RefreshScope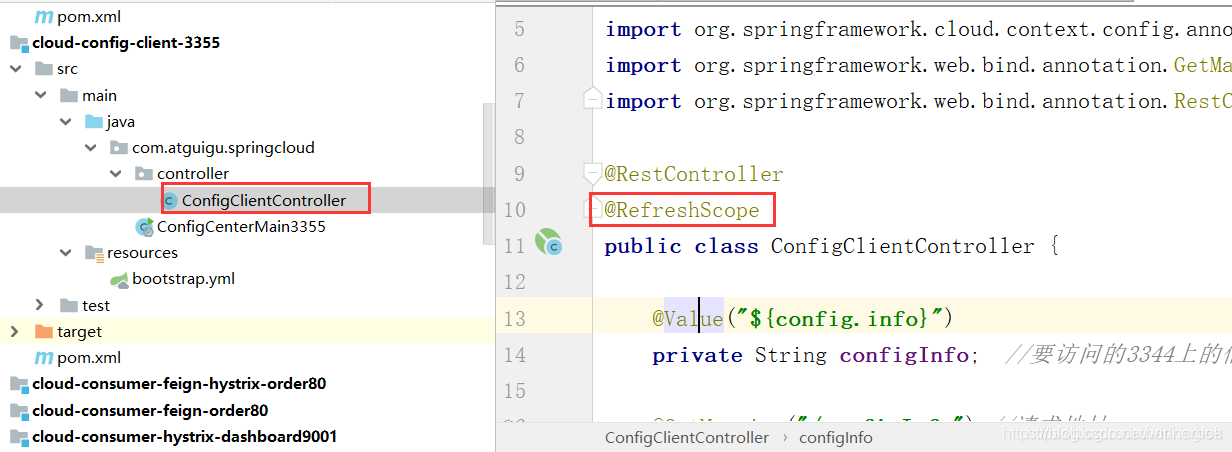
4、测试
这里我们修改以下github上配置的版本信息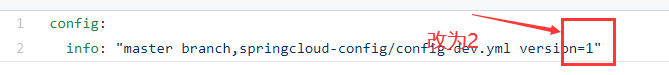
再来访问一下3344项目的总配置,发现改变了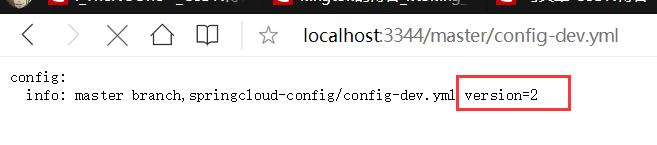
当我们访问3355项目的得到配置呢?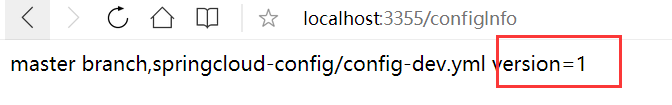
发现还是1,这里就需要给3355发一条post请求来激活动态配置
这里往命令窗口扔一条命令即可
curl -X POST “http://localhost:3355/actuator/refresh”
成功刷新配置信息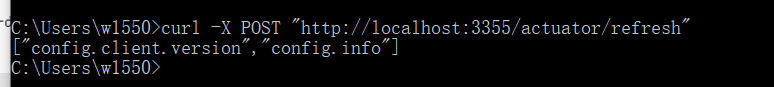
前言
分布式系统棉铃的—配置问题
微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务。由于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能运行,所以一套集中式的、动态的配置管理设施是必不可少的。
SpringCloud提供了ConfigServer来解决这个问题,我们每一个微服务自己带着一个application.yml,上百个配置文件的管理…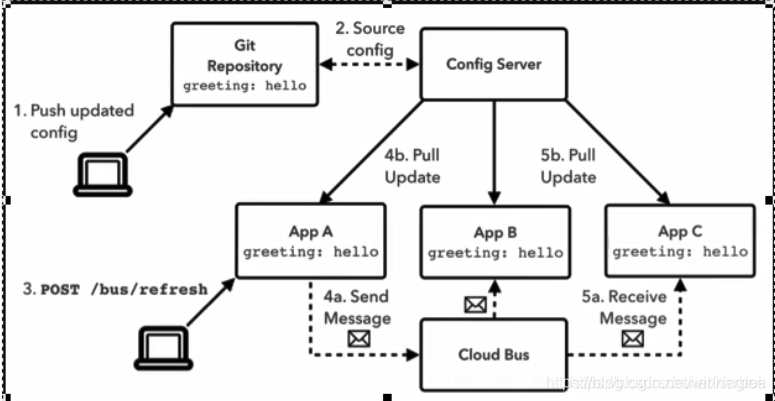
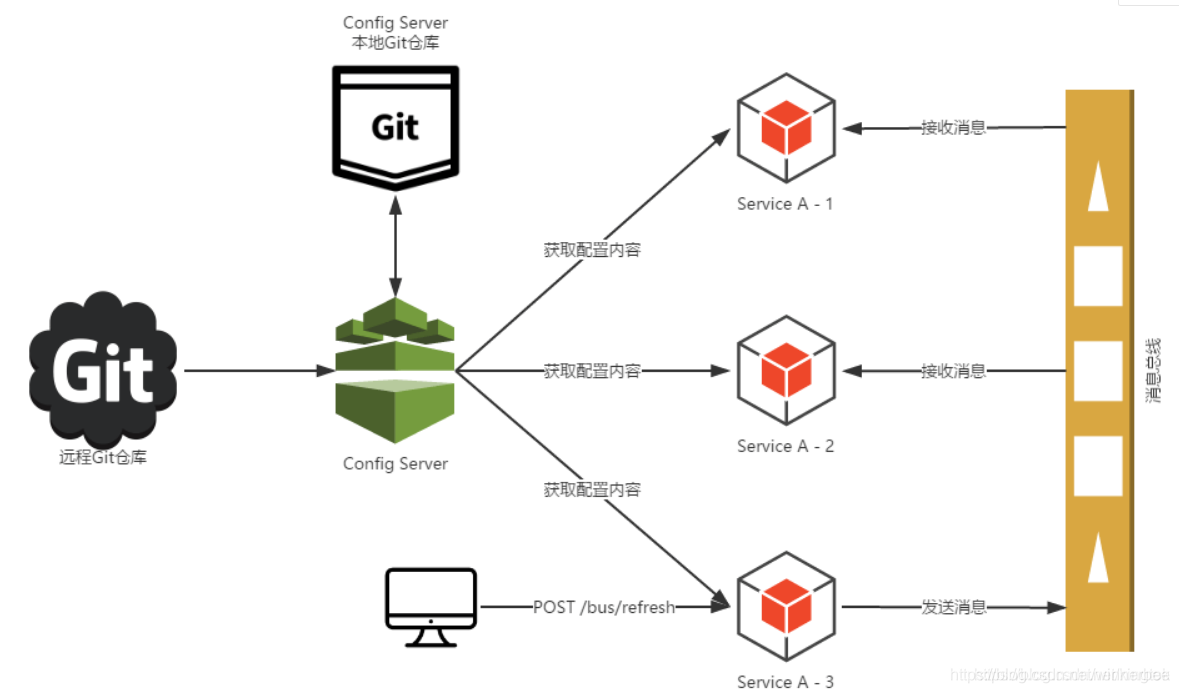
Spring Cloud Bus是用来将分布式系统的节点与轻量级消息系统链接起来的框架,
它整合了Java的事件处理机制和消息中间件的功能。Spring Clud Bus目前支持RabbitMQ和Kafka。
什么是总线?
在微服务架构的系统中,通常会使用轻量级的消息代理来构建一个共用的消息主题,并让系统中所有微服务实例都连接上来。由于该主题中产生的消息会被所有实例监听和消费,所以称它为消息总线。在总线上的各个实例,都可以方便的广播一些需要让其他连接在该主题上的实例都知道的消息。
基本原理
ConfigClient 实例都监听MQ中同一个topic(默认是springcloubus),当一个服务刷新数据的时候,它会把这个信息放入到Topic中,这样其他监听统一topic的服务就能得到通知,然后去更新自身的配置。
RabbitMQ 的安装
https://blog.csdn.net/ftdd_hw/article/details/80082790
项目
1、目录结构
2、改POM
3、建application.yml
4、主启动类
5、业务类
6、运行代码
热门文章
- 12月8日→20.5M/S|2024年最新免费节点Free V2ray订阅链接地址
- 宠物美容去哪里学(哪有学宠物美容)
- 2月2日→18M/S|2025年最新免费节点Free V2ray订阅链接地址分享
- 中牧股份的疫苗怎么样(中牧疫苗销售点有哪些)
- 全国动物疫苗生产厂家有哪些公司 全国动物疫苗生产厂家有哪些公司名称
- 动物疫苗可以自己打吗多少钱一针啊图片(动物打疫苗 人还打吗)
- 动物疫苗的种类和研发过程视频讲解(动物疫苗的种类和研发过程视频讲解图)
- java springMVC之@RequestMapping注解
- 1月3日→18.6M/S|2025年最新免费节点Free V2ray订阅链接地址分享
- vue3使用ref获取元素